Weekly Report 1Apr2011
From RHESSI Wiki
RHESSI Albedo Imaging Test
The test below was done with the follwing conditions:
- Three input maps were create:
- A compact circular Gaussian Source
- A compact Circular Gaussian Source overlaid with a concentric extended Circular Gaussian Source
- A compact Circular Gaussian Source with an extended Circular Gaussian Source offset towards the disc center
- In the cases with two sources the number of counts in each source was equal
- Calibrated Eventlist Files were made from each map
- A Clean image was made from each CBE using the following parameters:
- Time: 20-Feb-2002 11:06:10 - 11:06:40
- Energy: 15keV - 25keV
- Detectors: 1 to 9
- Clean Beam Width Factor: 2
- A Back Projection Image was created for each detector for each of the three Clean Images
- The location of the pixel in the Heliocentric X coordinate with the maximum flux was recorded for each Back Projection image
Results
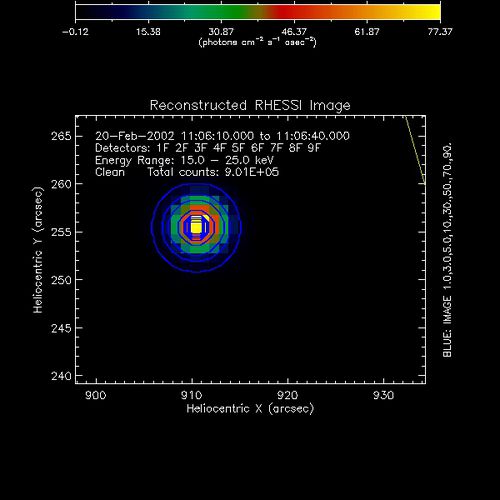
The image below shows the Clean image for a single compact circular Gaussian source. The contours for the original map are overlaid in blue.
The Clean image is larger than the 1% contour of the original map. This is due to the noise added by the coarser grids for a source that can be accurately imaged using just detectors 1 to 3.
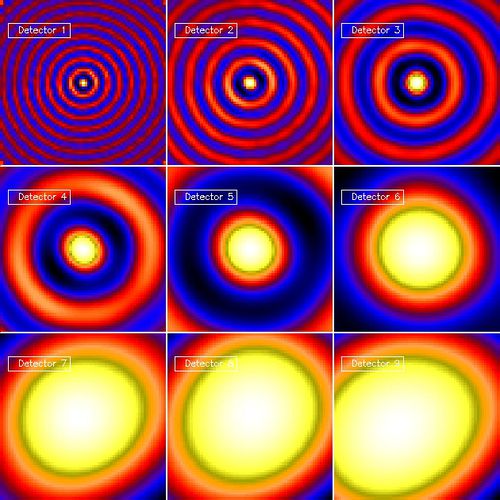
The images below show the Back Projection for each detector in the case of the compact Circular Gaussian Source.
In the finer grids the side lobes due to back projection are present. In the coarser grids. The source gets smeared out until it approaches the size of the Field of View. A discussion of the location of the pixel with the maximum flux follows below the final plot.
The image below shows the Clean image for a compact circular Gaussian source overlaid with a concentric circular extended Gaussian Source. The original map is overlaid in blue contours.
Clean creates an image that has a larger FWHM than the compact source alone so it is accounting for additional flux from the extended source, however the 1% contour of the original map on the same color scale as the image for the compact source alone is larger than the image. As the extended source becomes weaker the counts drop off more quickly.
The images below are the Back Projection images for each detector for a map containing a compact source overlaid with an extended source.
Once again we observe the same patterns as seen with just a compact source. The finer grids image a compact source with side lobes, while the coarser grids show a smeared out source. It is difficult to observe any difference between these and the images for just a compact source. The results for the maximum pixel location are similar as shown in the final plot.
The Clean image below is for a compact circular Gaussian source and an extended circular Gaussian source offset toward the disk center by 6 arcsec. The contours overlaid are the original map.
The Clean image shows the circular source bleeding into the extended source towards the disk center. The images show the characteristics of the original map, with a small source with concentrated flux and a larger more diffuse source separated from it.
The Back Projection images for each detector are shown below.
In this test the differences between the single source and the concentric sources can be seen in detectors 2,3, and 4, clearly. The compact source at the center of the image is no longer circular and the side lobes are not circles. The locations of the maximum pixels are discussed below.
The plot below shows the Heliocentric X location of the maximum pixel for each Back Projection image for a single detector in all three map configurations.
- The clearest differences are seen in detectors 4,5, and 6. The maximum pixel is in a position between the extended and compact sources in the offset case. In the concentric case and the compact case The values are the equal for these detectors.
- For the finer grids the position for the offset and compact cases are the same. This is reasonable since the finer grids just seeing the compact source. In the offset case additional counts from the extended source do create a measurable effect. In the concentric case the position is slightly sifted. This is probably due to the extended source adding counts to the compact source , although this should be done symmetrically. I'm uncertain as why there is a shift.
- In the case of the coarser grids the image smeared out. I don't think the maximum can be taken as anything but variation due to noise in these cases.
Goals
- Try imaging methods with different detector combinations and maps, to see which methods can determine the shift of an extended source near the limb due to albedo or being a coronal source.
- Run Brian and Kim's imaging methods for 2003 flares